IP Address Reputation Basics

When the time comes to sell, buy, or lease an IPv4 address, multiple factors will come into play. The reputation of an IPv4 address block is a factor that is poorly understood and often ignored. Neglecting this factor can result in a block of addresses that have a limited usefulness and requiring significant additional effort to be usable.
An IP address’ reputation can significantly impact its utility and worth in the digital marketplace. A tarnished reputation can hinder email deliverability and even prevent businesses from operating online.
What is IP Address Reputation?
IP address reputation is a measure of the trustworthiness of an IP address based on the past behavior originating from that address. In some reputational systems the behavior of neighboring addresses will also affect the reputation.
Address reputation scoring is a measurement of the address’s historical behavior and associated activities. It functions similarly to a credit score in two significant ways. Like credit scores, there are multiple entities that assess the reputation and they do not always agree. The reputation is also generally reduced to a simple numerical metric to aid in decision making.
While this reputation might be invisible to the casual user it is an integral part of the defensive protections in many service providers. Networked systems import reputation lists and use them in combination with the operator’s policy to decide how to treat communication from IP addresses. While the most popular use of reputation is to evaluate if e-mail is spam, it can be used for other purposes including blocking all traffic completely.
IBM uses several classifications for types of behavior that will lead to a negative reputation:
- Anonymous proxies
- Botnet Command and Control Server
- Dynamic IPs
- Malware
- Scanning IPs
- Spam
Much like a bouncer at a bar checking IDs at the entrance, IP address reputation is used to decide whether to accept email or let consumers buy products. Access is denied when an address is on an RBL (Realtime Block List). But addresses with a clean reputation are welcome. Many organizations configure the IP addresses of their business partners and other important networks to an allowlist to avoid service interruptions.
Impacts of Address Reputation
When it comes to IP reputation management, three primary factors are impacted by address reputation:
- Email deliverability – A favorable reputation increases the likelihood that emails will reach an intended recipient’s inbox. Conversely, a poor reputation often results in the connection being closed before the message has even been sent.
- Network reachability – Some providers will prevent all communication from sources with a significantly bad reputation.
- Ranking – Much like in the real world, a good reputation online can open doors which will influence search engine rankings for SEO, enable smoother interactions with web services, and contribute to a positive user experience.
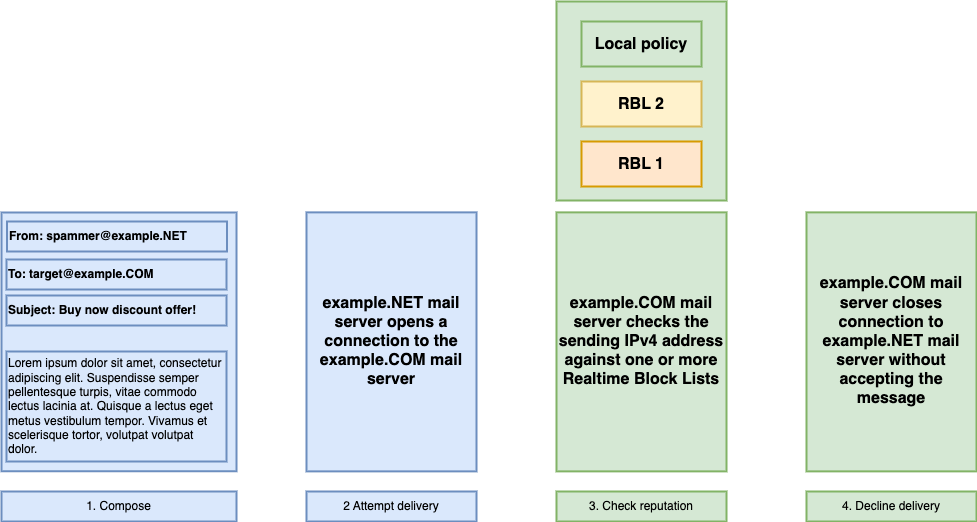
Organizations use IP address reputation in combination with their own policy when deciding whether to accept or reject mail and other data traffic.
Factors that Influence IP Address Reputation
Several elements are factored into the reputation equation, including:
- Record keeping – Malicious actors often hide behind inaccurate information. Prior usage of an IP address will have a major impact on its reputation. If it was previously associated with spamming, phishing, or other malicious activities, the new user of the address will need to correct the reputation. Ensuring that the RIR public records are updated is an important part of this.
- Attack traffic – If the address is used to attack another device, either as part of a denial of service attack or more direct hacking the reputation will be reduced.
- Spam complaints – The total number of spam complaints received against an IP address will impact its reputation—the more complaints, the worse the reputational score.
- Malware distribution or phishing attacks – If an IP address has been involved in distributing malware, hosting malicious content, or performing phishing attacks, it will have a diminished reputation.
Remote Block Lists: Gathering IP Address Reputation Information
Similar to credit reporting companies tracking financial history, RBLs track the digital history of an address. These databases maintain an active list of addresses that have been associated with unscrupulous behavior. If an address is granted this ignominious honor, it signals to all other sites and bots that the address may not be a trustworthy source. Most RBLs will automatically remove IP addresses shortly after they stop acting maliciously. All reputable RBLs provide a way to request a manual review and will not charge a fee for doing so.
Prominent RBL providers, such as Spamhaus, SpamCop, and SURBL, use different methodologies to evaluate IP address reputation. Some focus on the volume of spam, others on the nature of the spam, and yet others might look at additional factors such as user reports.
If an IP address block lands on an RBL, that status isn’t permanent. Addresses may cycle from malicious to benign and back several times over.
As WebRoot notes: “When looking at the top 50k IP addresses that recurred on our “malicious” list in 2020, 97.3% were caught displaying at least four distinct risk factors, such as spam sources. Almost half (45%) of the top 50K recurred during at least 2 different months, while 25.8% were seen doing something malicious every single month.”
Limitations of IP Address Reputation
It’s worth noting that IP address reputation isn’t a perfect system. It’s not infallible and can be prone to false positives and false negatives. Innocent IPs may be flagged as malicious, whereas bad spammers go undetected.
When purchasing an IPv4 address, itsreputation should be a guiding touchpoint rather than a final judgment on its trustworthiness.
Additionally, IP reputation isn’t static. It can be improved over time.
How to Improve IP Address Reputation
There are actionable steps an IP address owner can take to improve its reputation, including:
- Separate transactional and marketing emails – By segregating email domains, a business ensures that an issue with one doesn’t affect the deliverability of the other, especially since marketing emails are more likely to be perceived as unwanted or spam.
- Follow email sending best practices – To prevent emails from being marked as spam, organizations should follow best practices. The SendGrid bulk e-mail guide suggests:
- Use multiple IP addresses.
- Use a preference center.
- Ensuring you have explicit permission to e-mail your recipients.
- Practice good list hygiene and have a sunset policy.
- Authenticate your e-mail with SPF, DKIM, DMARC.
- Regularly check your reputation and blacklist status.
- Don’t send your subscribers too much mail.
- Leverage re-engagement campaigns.
- Ensure it’s something worth sharing.
- Practice proactive reputation management – If an issue is flagged, don’t let the problem fester. Instead, nip them in the bud by responding with alacrity to any report.
IPv4.Global—A Trusted IPv4 Broker
Whether you’re looking to buy an IPv4 address block with an assuredly clean reputation or looking to repair a block’s reputation before or after a sale, IPv4.Gobal is the trusted market leader. Our experts will guide you through the transfer process, which is a foundational step in improving a negative IP address reputation. We can also connect you with specialists who can help you contact blocklist operators if you need extra help.
Remember, an IP address’s reputation isn’t set in stone. If an IP address has a less-than-savory reputation—just as with a credit score—it can be gradually improved with time.
To discover more, reach out to our team today.